Cryogenic processing refers to using extremely low temperatures to treat materials or substances in various industries. It helps increase their resistance to wear, fatigue, and corrosion, making it a crucial process in industries requiring high precision and longevity levels.
It is essential in various industries, as it plays a vital role in the oil and gas industry, especially in liquefying natural gas for transportation and storage.
Cryogenics are fundamental in aerospace, where they are used in propulsion systems, such as rocket engines, and in the storage of rocket fuel.
It is pivotal in the medical field, particularly for cryopreservation, which involves freezing cells, tissues, and organs for later use.
In the food industry, cryogenic processing, such as cryogenic freezing, helps preserve food's taste, texture, and nutritional content.
Innovations such as energy-efficient cryogenic equipment, automation, and improved insulation materials have led to more efficient processes. These have minimized energy consumption and reduced environmental impact.
This blog explores the key technologies and innovations shaping the future of cryogenic processing. From new cryogenic cooling systems to breakthroughs in material science, we’ll explore the innovations driving the evolution of this critical technology.
#What Is Cryogenic Processing?
Cryogenic processing refers to the use of extremely low temperatures, typically below -150°C (-238°F), to treat materials or substances and enhance their properties.
The basic principle of cryogenic processing involves cooling substances to a temperature where their atomic structure is altered. This enhances specific physical properties. These low temperatures also transform gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and natural gas into liquid form, which allows for easier transportation and storage.
Overview of Cryogenic Applications
Let's take a look at some applications.
Gas Liquefaction (e.g., LNG Production)
Natural gas is cooled to cryogenic temperatures, typically around -160°C (-260°F), turning it into an easier liquid to store and transport.
This process helps expand the global energy market by allowing natural gas to be shipped across oceans in liquid form.
.jpeg)
Material Strengthening (Cryogenic Hardening)
This improves the performance and lifespan of materials like metals and alloys.
Materials experience increased strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and fatigue.
Preservation and Storage (Cryogenics in Healthcare)
Cryopreservation involves cooling biological samples, such as cells, tissues, or even whole organs, to cryogenic temperatures to stop biological processes and prevent degradation.
This technique is widely used in healthcare and medical research for organ transplantation, in-vitro fertilization (IVF), and preserving stem cells or genetic material.
Cryogenic technologies continue to evolve, impacting numerous industries by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and advancing sustainability.
These industries include:
Oil and Gas
Aerospace and Defense
Healthcare and Biotechnology
Food and Beverage
Electronics and Manufacturing
#Key Equipment in Cryogenic Processing
Cryogenic processing relies on specialized equipment designed to handle extremely low temperatures while maintaining efficiency, safety, and performance. Here are some of the key pieces of equipment used in cryogenic systems.
Cryogenic Storage Tanks
Cryogenic storage tanks are essential for the safe containment and storage of liquefied gases at extremely low temperatures. These tanks are designed to maintain the temperature of the liquid gas, preventing it from evaporating or boiling off.

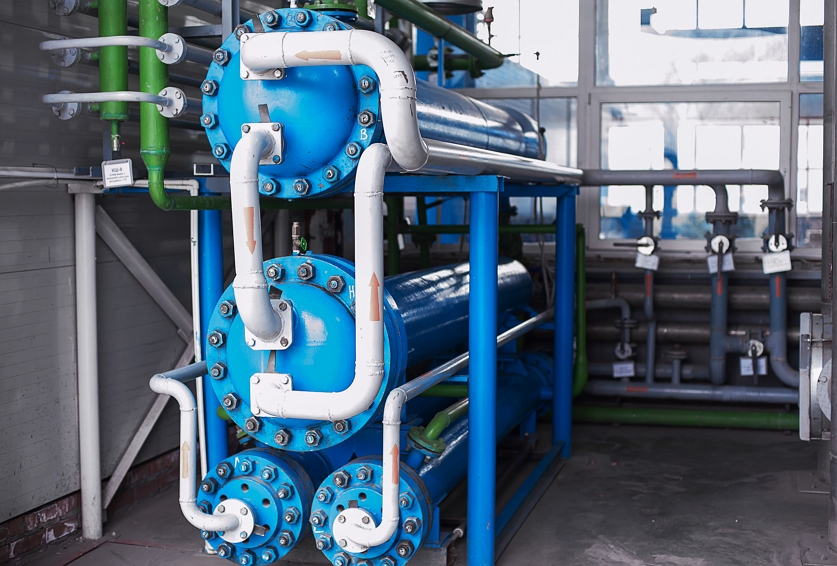
Cryogenic Pumps
Cryogenic pumps transfer and move cryogenic liquids and gases within a system. They must operate efficiently at extremely low temperatures while preventing the gas from warming up and vaporizing.
Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are vital components in cryogenic systems. They allow the transfer of heat between two fluids without mixing them. They are particularly important for cooling or heating cryogenic gases, helping to manage the system's temperature efficiently.

Cryogenic Expanders
Cryogenic expanders, also known as turboexpanders, are devices used to extract energy from the expansion of cryogenic fluids. When a high-pressure cryogenic liquid expands, it cools significantly, which can be harnessed for work or further cooling.
Cryogenic Insulation Technologies
Cryogenic insulation is crucial in maintaining the ultra-low temperatures required in cryogenic processing. Effective insulation minimises heat transfer from the surrounding environment, preventing the liquid from warming up or vaporising.
Types of Insulation
Vacuum Insulation: Often used in the double-walled construction of cryogenic storage tanks, where the space between the walls is evacuated to create a vacuum, thus reducing heat transfer.
Foam Insulation: Some cryogenic systems use polyurethane or other insulating foams to reduce heat transfer, particularly in pipelines and smaller equipment.
Superinsulation: A layer of superinsulation, made from materials like multi-layer insulation (MLI), is often used for specialised cryogenic containers and systems, such as spacecraft or high-performance LNG pipelines.
#Innovations Shaping the Industry
Innovations in cryogenic technology are pushing the boundaries of what is possible, offering exciting new possibilities across a wide range of industries.
These advancements are shaping the future of cryogenic processing, from improving energy efficiency and sustainability to enhancing the performance of cryogenic systems.
Below are some of the key innovations shaping the industry today:
Advanced Cryogenic Materials: These new materials can withstand extreme cryogenic temperatures while maintaining or enhancing performance. These materials improve the efficiency, safety, and longevity of cryogenic systems.
Energy-Efficient Cryogenic Systems: Advanced cryogenic compressors, with improved materials and designs, are reducing energy losses during gas compression. More advanced turboexpanders are helping to recover more energy from cryogenic processes, reducing the need for external energy input.
Flexible Cryogenic Storage Systems: New developments in flexible, modular cryogenic storage systems allow for more scalable and adaptable solutions in industries like LNG and healthcare.
Industry Applications and Examples
Cryogenics is used in various industry applications, some mentioned below.
LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas)
Cryogenics plays a pivotal role in the liquefaction of natural gas, which is key to its transport and storage. Liquefying natural gas makes it easier and more economical to store and transport over long distances, especially where pipelines are not feasible.
Cryogenic technology ensures that natural gas remains liquid throughout the entire transport process, from the liquefaction facility to end-user markets.
As the global demand for LNG continues to grow, significant advancements are being made in LNG carriers and onshore liquefaction facilities.
Modern LNG carriers use sophisticated membrane technology, lining the tanks with highly effective cryogenic insulation.
A growing trend in LNG carrier design is the use of dual-fuel engines. These engines can run on LNG itself, reducing reliance on conventional fuels like diesel.
One of the key innovations in onshore liquefaction facilities is the modularisation of plant components.
Modular liquefaction plants are being designed with pre-fabricated, scalable modules that can be easily assembled and expanded.
Cryogenic expanders are being integrated into the liquefaction process to recover and reuse energy that would otherwise be lost as heat.
Aerospace
Cryogenics plays an essential role in modern rocket propulsion systems, contributing significantly to the efficiency and performance of space exploration missions.
The use of cryogenic fuels, particularly liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen, has revolutionized space travel due to their high energy density and efficiency.
The combination of these fuels allows for longer-duration missions, as the fuels’ high specific impulse reduces the fuel required for a given amount of thrust.
Efficient cryogenic fueling is crucial for space exploration missions, from launching rockets into orbit to powering spacecraft during deep space missions.
Innovations in super-insulated cryogenic tanks have greatly improved the efficiency of storing liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen, and other cryogenic propellants.
Cryogenic refueling systems in space missions are becoming increasingly automated, allowing for more precise and efficient fueling operations.
Food and Beverage
Cryogenic freezing has revolutionized the food and beverage industry by providing advanced solutions for food preservation, quality maintenance, and processing.
This freezes food almost instantly, reducing ice crystal formation and preserving the food’s natural texture and flavor.
Cryogenic freezing is often used to preserve fruits and vegetables, especially delicate varieties as well as meat and seafood.
Liquid nitrogen systems play a crucial role in various food processing applications, enhancing both product quality and processing efficiency.
Liquid nitrogen is used for rapidly chilling or freezing food items, especially those that need to be cooled quickly to ensure they are safe for consumption and storage.
It is also used in cryogenic grinding or milling, which involves freezing materials like spices, herbs, and food ingredients to make them brittle and easier to grind.
#Challenges in Cryogenic Processing
While cryogenic processing offers numerous benefits across industries, implementing and maintaining cryogenic systems presents several challenges.
Here’s a look at some of the key obstacles faced in cryogenic processing:
High Energy and Operational Costs: The cooling required to maintain cryogenic temperatures is energy-intensive, which can lead to high operational costs.
Technological Complexity and Maintenance: Managing the delicate balance between temperature, pressure, and other environmental factors can be a significant challenge.
Safety and Handling Concerns: Cryogenic liquids present significant safety risks due to their extreme cold and potential for hazardous reactions.
Limited Scalability and Flexibility: While they have been widely adopted in certain industries, scaling up cryogenic processes to meet higher demands or adapting them to different applications can be challenging.
Addressing these challenges through innovation and improved safety protocols will be key to the continued success and widespread adoption of cryogenic processing across industries.
#The Future of Cryogenic Processing
Cryogenic processing is already a vital part of numerous industries, but as technology advances and global demands shift, the future of cryogenics holds even more potential.
One of the most significant shifts in the future of cryogenic processing is its integration with renewable energy sources to reduce environmental impact and ensure long-term sustainability.
Cryogenics will continue to play a vital role in space exploration and rocket propulsion. However, the future promises even greater advancements, as new technologies emerge to support the growing ambitions of space agencies.
The food and beverage industry will continue to benefit from cryogenic freezing and liquid nitrogen systems. As demand for fresh, high-quality, and sustainably processed foods rises, cryogenic technologies will evolve to meet these needs.
The cryogenic industry is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of science, technology, and sustainability.